Case Studies BHP Rail Training
Rail Shunting and Driving
Background
This project was established to produce a set of Virtual Reality (VR) and
Simulation experiences to assist and enhance the BHP Rail Training
Curriculum for Rail Shunting and Driving courses.
Virtual Reality Training
The training program supports rail unit competency within Certificate II and
III – Rail Operations, developing the skills and knowledge for safe rail
operations as per regulatory requirements.
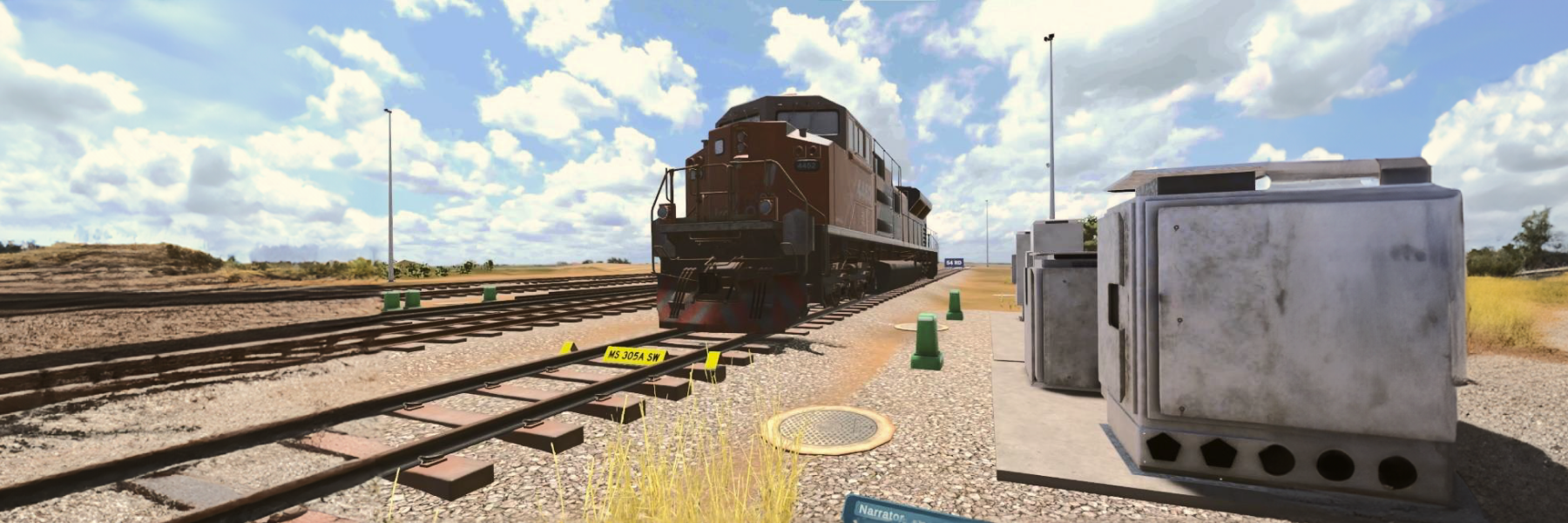
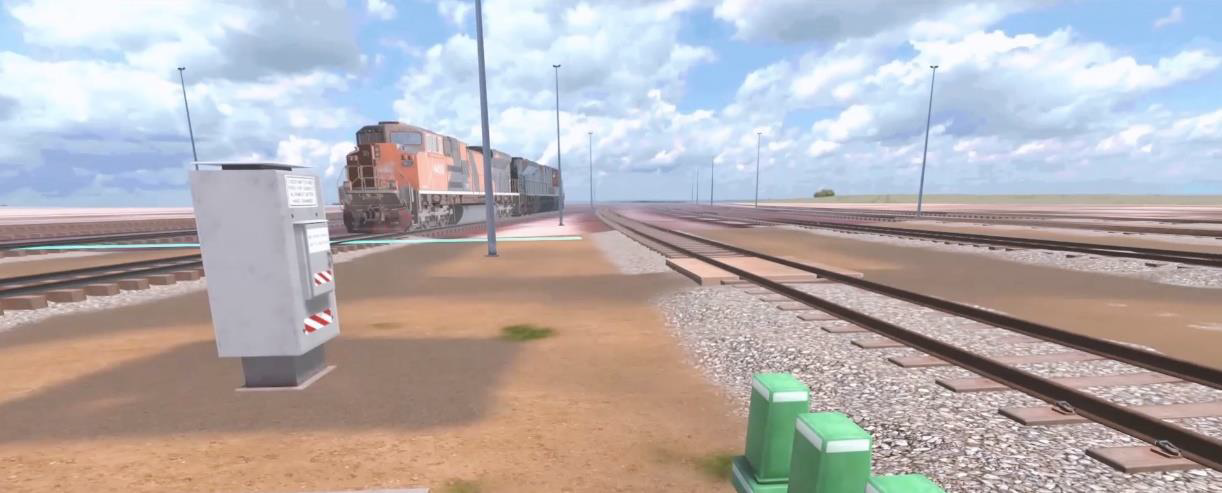
The VR training experience is set on a virtual rail track to educate drivers in
hazard identification, yard operations, primary rail activities and safety
systems, safety equipment, roll-by inspections, and shunting. In addition, Rail Simulations develop learners’ confidence and skill in train driving
including testing and applying braking systems, responding correctly to
signals, stopping and starting, and following the correct procedures for car
dumping.

Benefits
These VR and Simulation experiences are perfectly placed to explore high-risk, high-consequence
activities in a safe virtual environment. These experiences assist the
training of highly skilled shunters and drivers who demonstrate best practices, a
result of repeatable procedural training sessions. The opportunity to provide
advanced skills development is available through customisable scenarios.
"...explore high-risk, high-consequence activities in a safe virtual environment..."
Telemetry
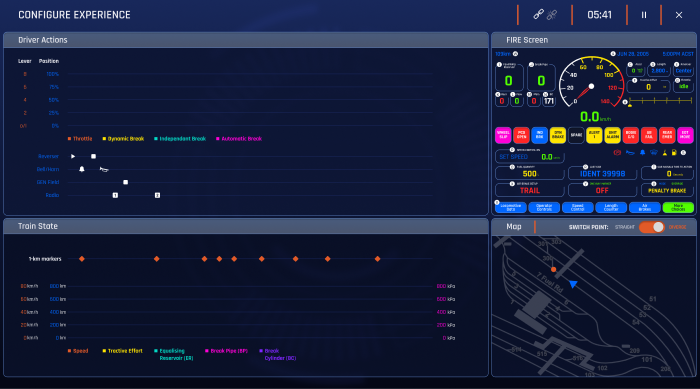
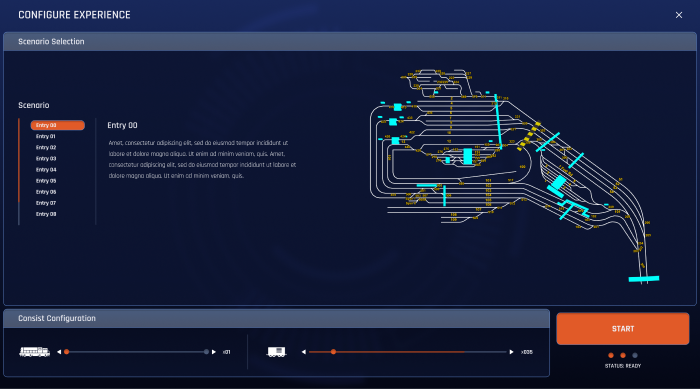
The virtual reality simulation is linked to a telemetry system providing real-time performance analytics allowing trainers to monitor each learner through their training.
The telemetry dashboard describes:
- A sequence that shows a high-level summary of the scenario.
- A log that shows the actions of the VR learner.
- Controls for scenario management and situation customisation.
- Statistics on train behaviour such as speed and brake pressures.
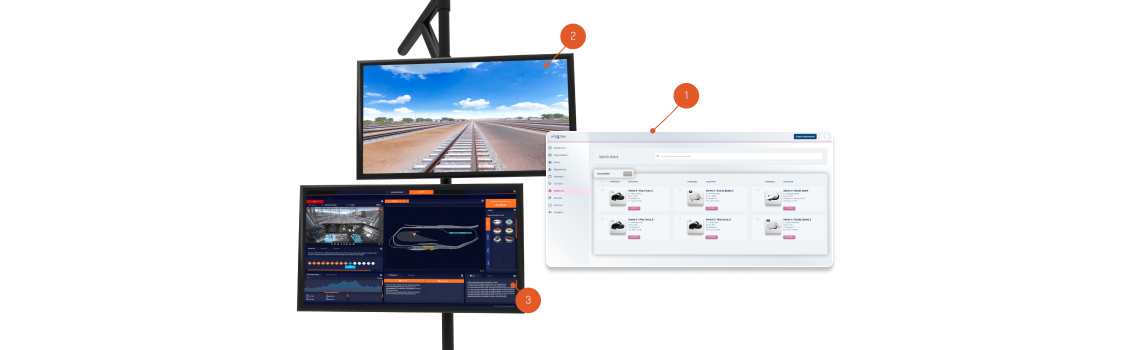
Hardware
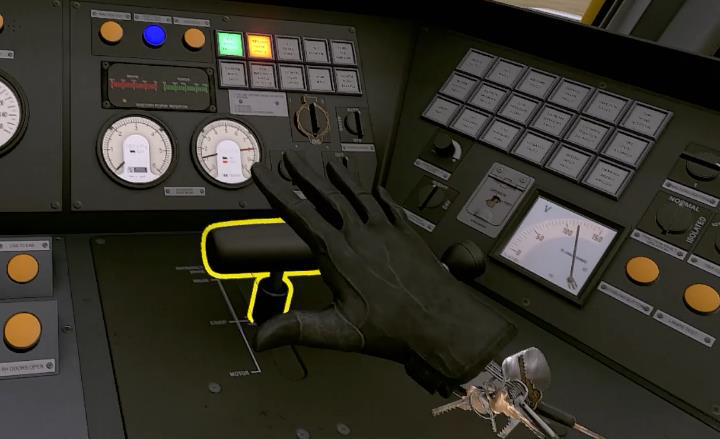

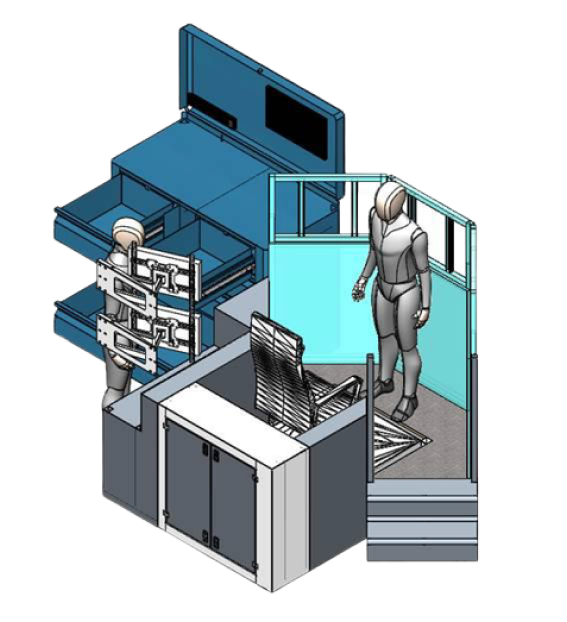
The VR learner uses a virtual reality headset to view the simulation experience. The learner can freely look around the cab and lean closer to or further away from the operator’s console. The headset alignment and VR learner’s seated position will be calibrated at the beginning of each session to ensure they can see clearly and can comfortably reach all required controls.
The learner is seated in a motion platform, which will move and rotate to emulate real train movement.
HTC Vive Pro (VR Headset):
This choice
was made due to its industry-wide use
and appeal. It provides exceptional value
with its high resolution, ideal for viewing
detailed environments such as a cabin
control panel.
Index Controllers (VR Controllers):
Intuitive handheld controllers allow the learner
to interact within virtual environments with ease and intuition.
 BASETEN
BASETEN
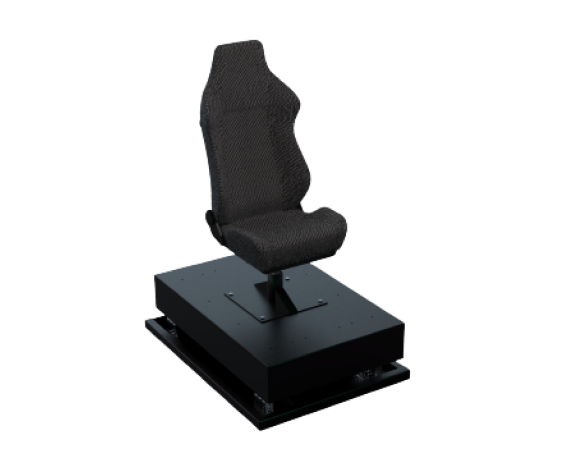 Motion Platform
Motion Platform
Motion Platform:
Powered by hydraulics, the
seated platform gives learners the perceived
experience of motion along the horizontal axis. The
hydraulics will respond directly to feedback from the
simulation, specifically when the VR learner
accelerates or applies breaks while driving.
VR Sensors:
Critical to providing function to the VR headset/controllers are the
sensors. Sensors help the headset and controllers track the exact
location/movement to match the actions of the
learner in the physical environment and affect what
they are experiencing inside the simulation.
Introduction to VR
The introductory experience uses the rail office and yard to familiarise the learner with key virtual reality safety protocols, and core navigation and interaction methods.
Adjusting the VR hardware for safety and comfort is essential before the learner is taken trackside to learn:
- How to navigate within VR.
- Interact with the environment.
- Gather information.
- Respond to stimuli.
This requires the learner to demonstrate competency in using VR mechanics and describe the importance of VR safety.
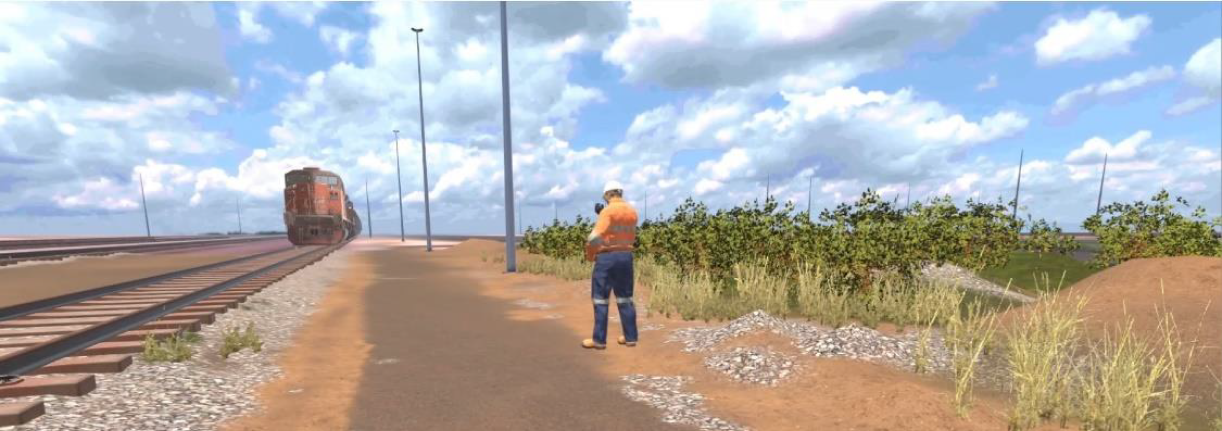
Fatigue Management
The Fatigue Management experience introduces the recognition of fatigue and the impact of fatigue-related incidents.
Through interaction with VR characters, the learner is prompted to identify signs of fatigue in a virtual co-worker and demonstrate strategies that could be employed to mitigate risk in the workplace. Through a virtual microsleep, the learner is placed in a potential catastrophic position, emphasizing the importance of continual vigilance when working in the rail yard.
Completion of this experience centres on the learner demonstrating a clear understanding of the personal and rail safety implications related to fatigue.
Drawing from competency criteria related to TLIF2010 Apply fatigue management strategies , this experience is highly relevant to a broad range of Transport and Logistics Training up to advanced certificate IV including TLI21921 and TLI21918 Certificate II & III in Track Protection.
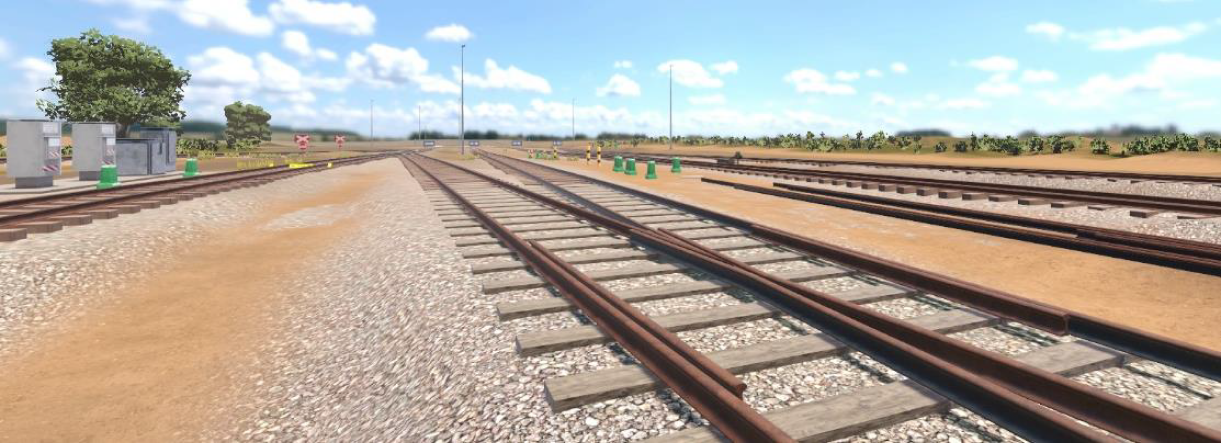
Rail Hazard Identification
Rail Hazard Identification is an experience that allows the learner to practice situational awareness and embed safe work practices.
In this scenario, the learner identifies essential PPE while in the office. When navigating across the rail yard, the learner discovers environmental conditions that prevent working in the rail corridor and explores safe places and danger zones involved when crossing track and moving around the yard. Hazardous situations examine learners’ continual vigilance and situational awareness throughout this experience.
Demonstrating safe work practices and following the required procedures while working in the rail safety corridor is core for those working in the rail yard.

Drawing from competency criteria related to TLIF0020 Safely access the rail corridor , this experience is highly relevant to a broad range of Transport and Logistics Training up to advanced certificate IV including TLI21921 and TLI21918 Certificate II & III in Track Protection.
Yard Operations
Yard Operations provides two avenues in which to familiarise the learner with the rail yard. Initially, the learner explores the yard via an interactive map after which they move on to navigating around the virtual yard.
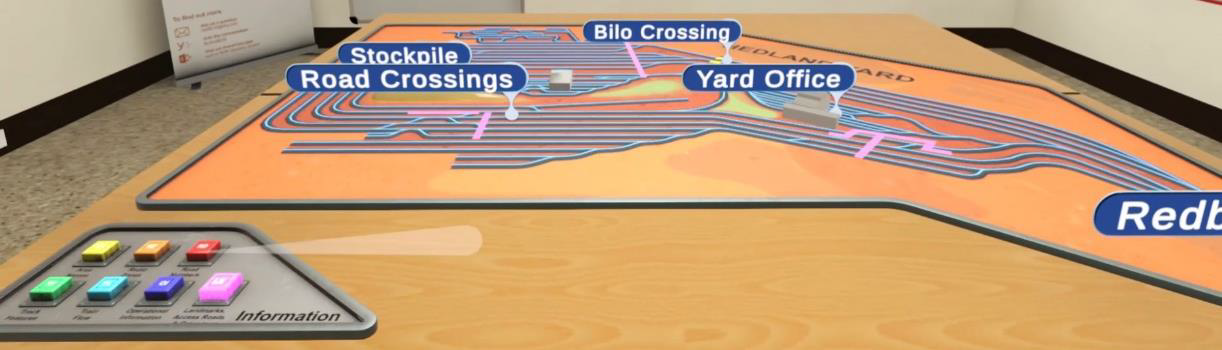
This experience allows the learner to safely explore three main areas of the rail yard identifying landmark features, areas, road names, tracks, and track features, access roads, crossings, danger zones, and more. In exploring the locations and features, learners will be exposed to key terminology, and operational and track level features of the rail yard.
The takeaway from this experience is learners will be site-ready, starting work familiar with the locations and landscape in which they will be engaged.
This experience is highly relevant to a broad range of Transport and Logistics Training up to advanced certificate IV, drawing from competency criteria related to TLIB0013 Apply knowledge of rail operation fundamentals in yards or sidings .
Primary Rail Activities
In this experience, the learner is introduced to the Primary Rail Activities involved in being a shunter. Initially, the learner observes the process of shunting via an interactive map. The learner then moves on to navigating around the virtual yard to experience shunting up close.
The learner navigates through three locations in the rail yard learning how to direct train movements, break up trains into rakes (or put together rakes to become trains), perform roll-by inspections, and cut out bad order cars for servicing.
In completing this experience, the learner can describe the activities undertaken by shunters.

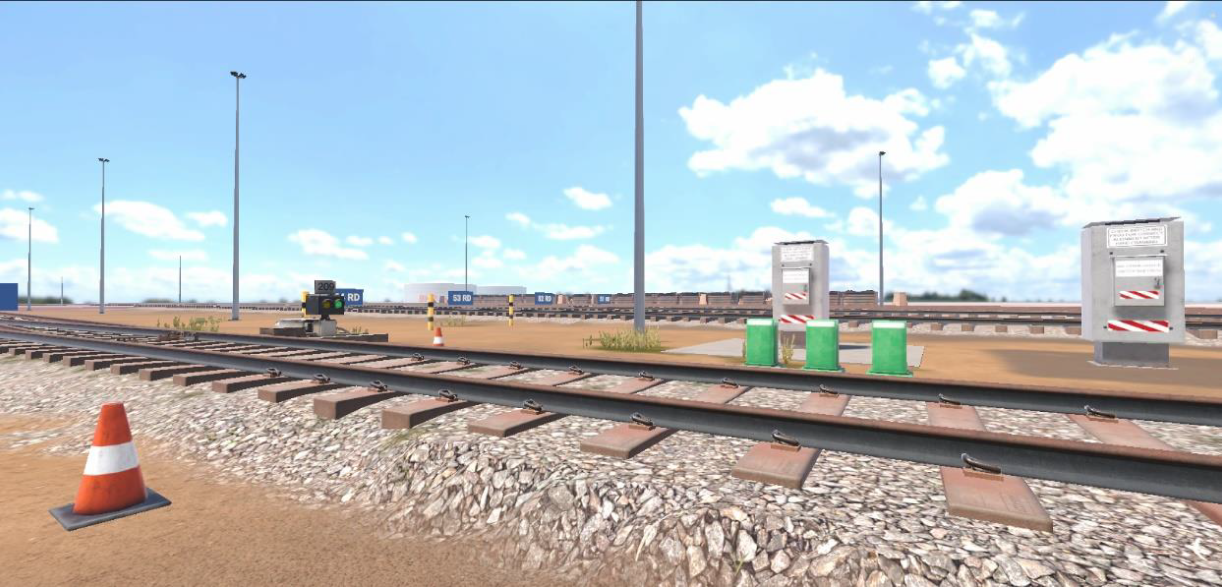
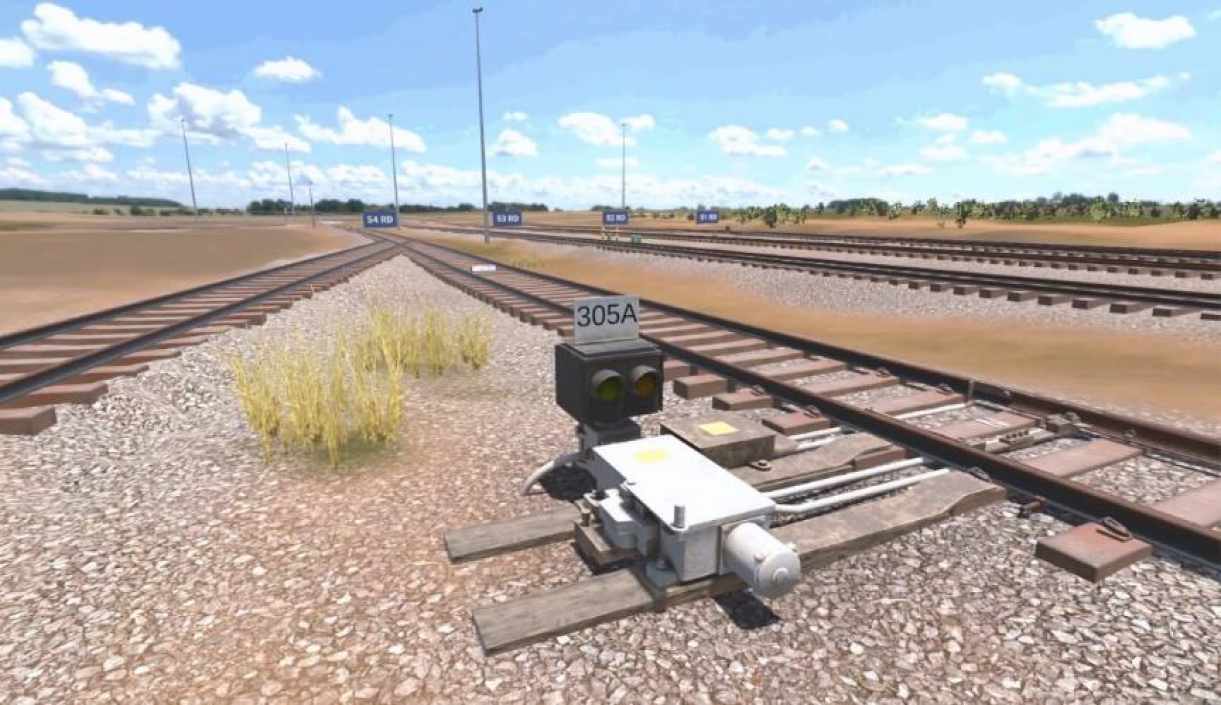
Rail Safety Equipment
Rail Safety Equipment is essential to shunting and driving.

The learner is introduced to key rail safety equipment found in the rail yard and along the tracks. The primary equipment featured in this experience includes the point clamps, derailers, wheel chocks, clearance markers, and the components of the turnout.
On completion, the learner can relate the purpose and function of this equipment, describe the safety impact if these devices are not used, and identify if the device has been deployed correctly.
This experience is highly relevant to a broad range of Transport and Logistics Training, drawing from competency criteria related to TLIW2041 - Clip points and apply rail safety equipment.

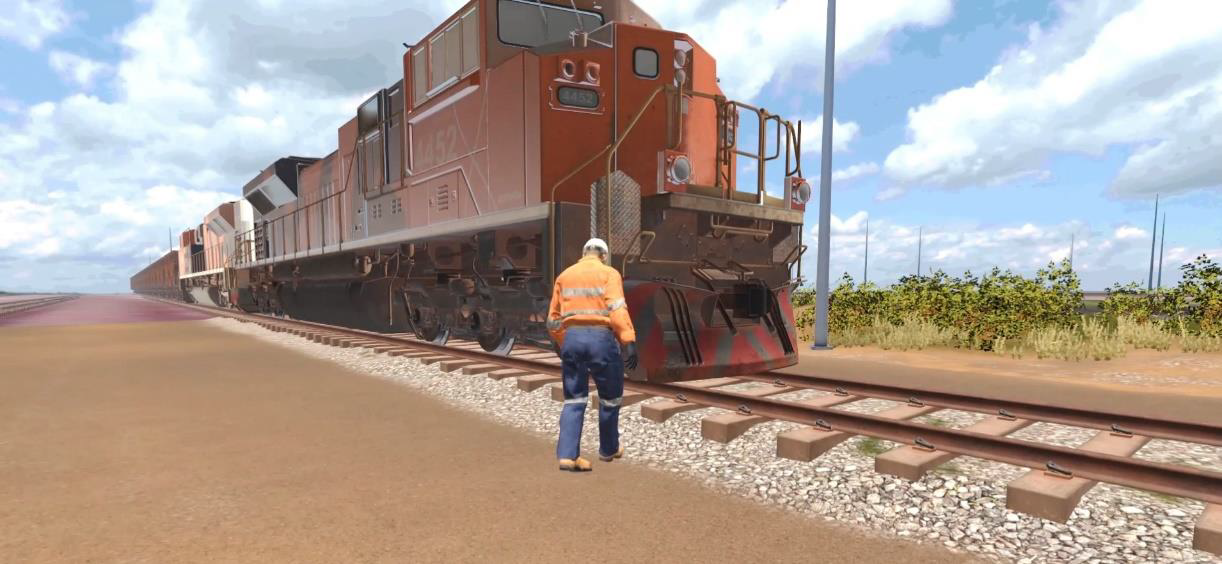
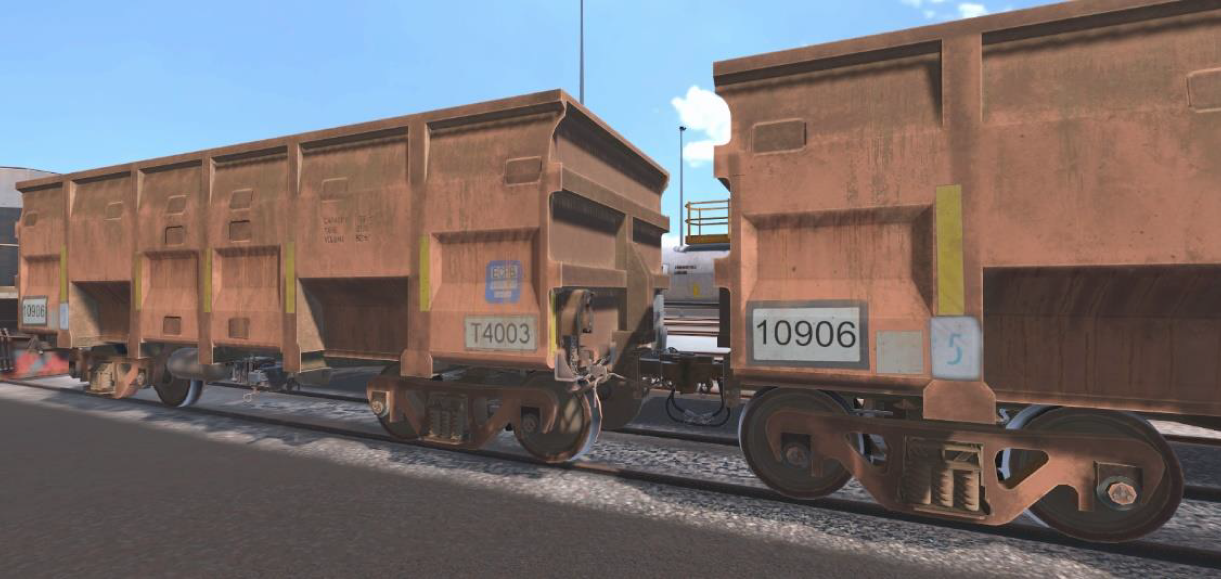
Conduct Train Roll-by Inspections
Performing a Roll-By inspection is an essential task for the Rail Yard.
In this experience, the learner will demonstrate the correct process for safely performing a roll-by inspection. The learner is engaged in identifying defects and faults through sight or sound, exhibiting the levels of patience and concentration required to perform this task successfully. To increase the engagement and improve the capacity of the learner, this experience has 4 speeds in which to perform the inspection, allowing the learner an opportunity to progress from beginner competency level to an advanced level required on the job.
This experience is highly relevant to a broad range of Transport and Logistics Training, drawing from competency criteria related to TLIB3021 - Conduct train roll-by inspection.
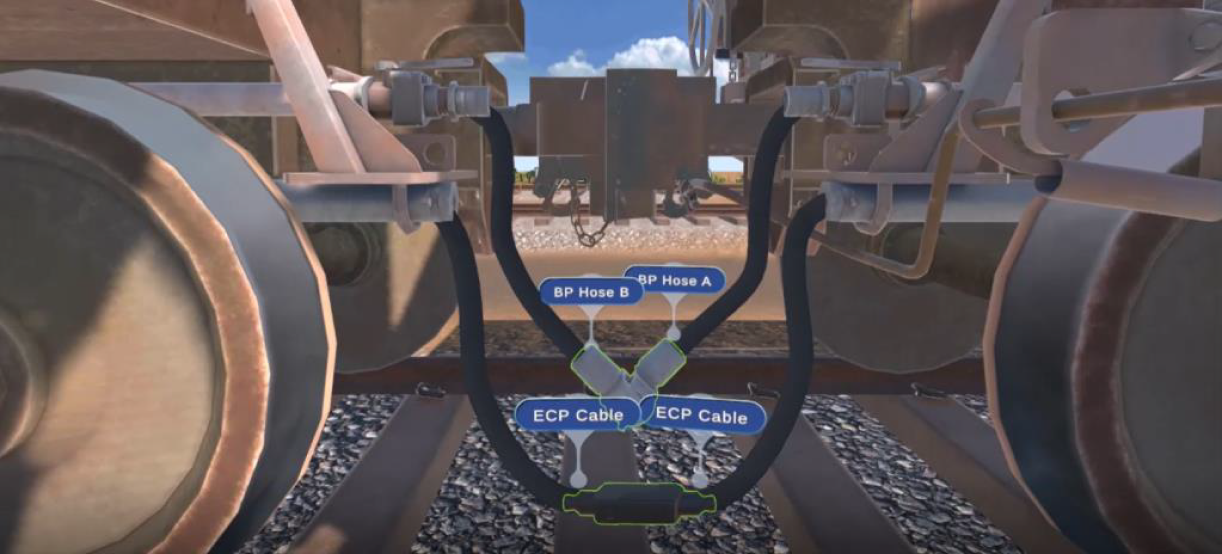
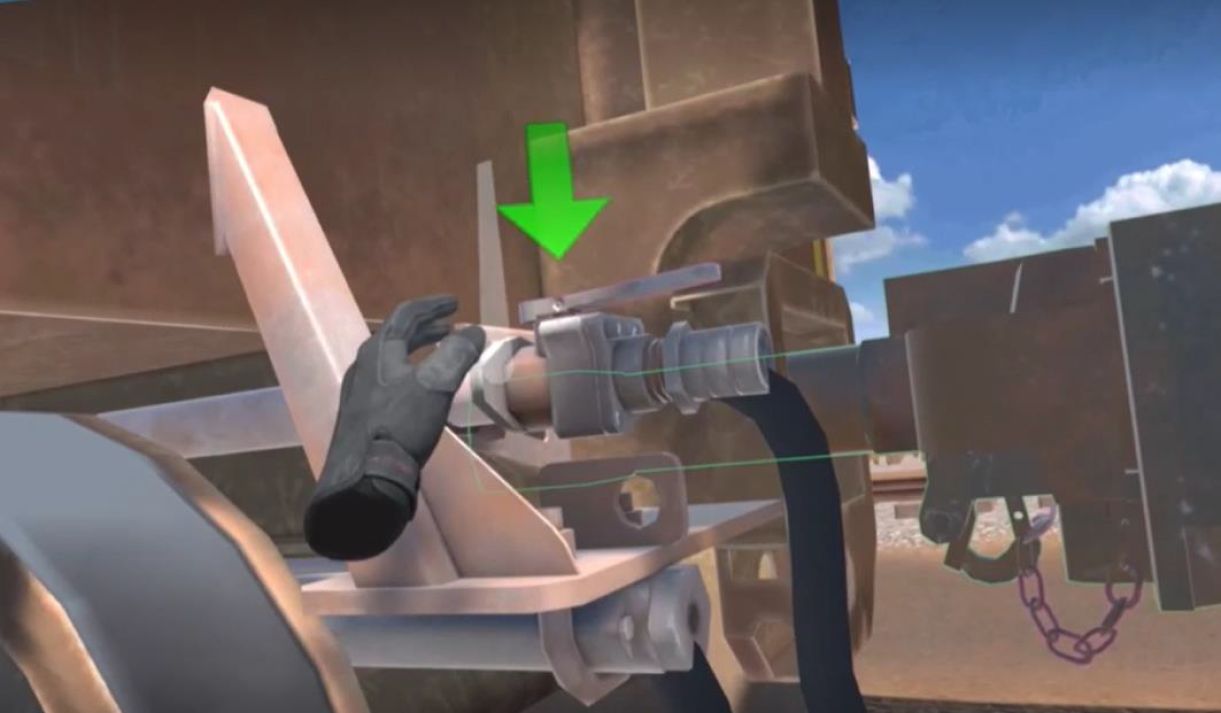
Shunt Rolling Stock
This experience looks at the skills and knowledge to safely shunt rolling stock.
The learner revises safety processes and engages in good radio communications. This experience requires the learner to perform a range of activities including uncoupling cars, coupling cars, and a stretch test. The focus is on best practices, following the correct processes, and demonstrating good communication to complete this activity successfully.
This experience is highly relevant to a broad range of Transport and Logistics Training, drawing from competency criteria related to TLIC3017 - Shunt rolling stock.
Rail Simulation
The Rail Simulation forms a core component of train driving skills development.
This VR simulation will accelerate skills development for train operators. The VR experience enhances existing training by allowing learners to familiarise themselves with the console controls, processes and procedures, hazards, and routes in a safe, virtual environment. A range of scenarios take the learner through console familiarisation, brake testing, moving and stopping a train, car dumping, and allow for freeform driving across a customizable route. This flexibility allows the trainer to increase complexity and test the trainee driver’s ability to respond to changing situations and potential distractions.
This experience is highly relevant to a broad range of Transport and Logistics Training up to advanced certificate IV in Train Driving.















